Rule Engine Walkthrough
This section details the end-to-end process of how the Underwriting Service evaluates a user for eligibility.
Rules and Rulebooks
Rules are the individual logic blocks that evaluate a user’s eligibility for Floats or Installment Loans. Rulebooks are a collections of rules that can approve a user for a Float or Installment Loan. Rulebooks are created as a means to approve users. Only one rulebook needs to approve a user for that user to be approved for a Float or Installment Loan.
With the exception of the primary rulebook (superseding rulebook). The primary rulebook must always pass, along with another regular rulebook, for a user to be approved for a Float or Installment Loan.
Rulebooks are configured by the rulebook yaml file in the rulebooks directory. It defines rulebooks and specifies the rules to be used, the priority order, any specific properties for a specific rule, and the type of rulebook (float or loan).
How Rulebooks are evaluated.
Rulebooks are evaluated by the priority order specified in the rulebook yaml configuration. If a rule fails, the entire rulebook fails. If a rule has an error, that error is surfaced to the rulebook level and the rulebook fails. If all rules pass, the rulebook passes.
The first rulebook (besides the primary rulebook) to approve a user is marked as the deciding rulebook. All the rulebook results are stored in Dynamo for later use.
Process Flow
The underwriting process is asynchronous and event-driven. It involves two main stages: Rule Execution and Result Aggregation.
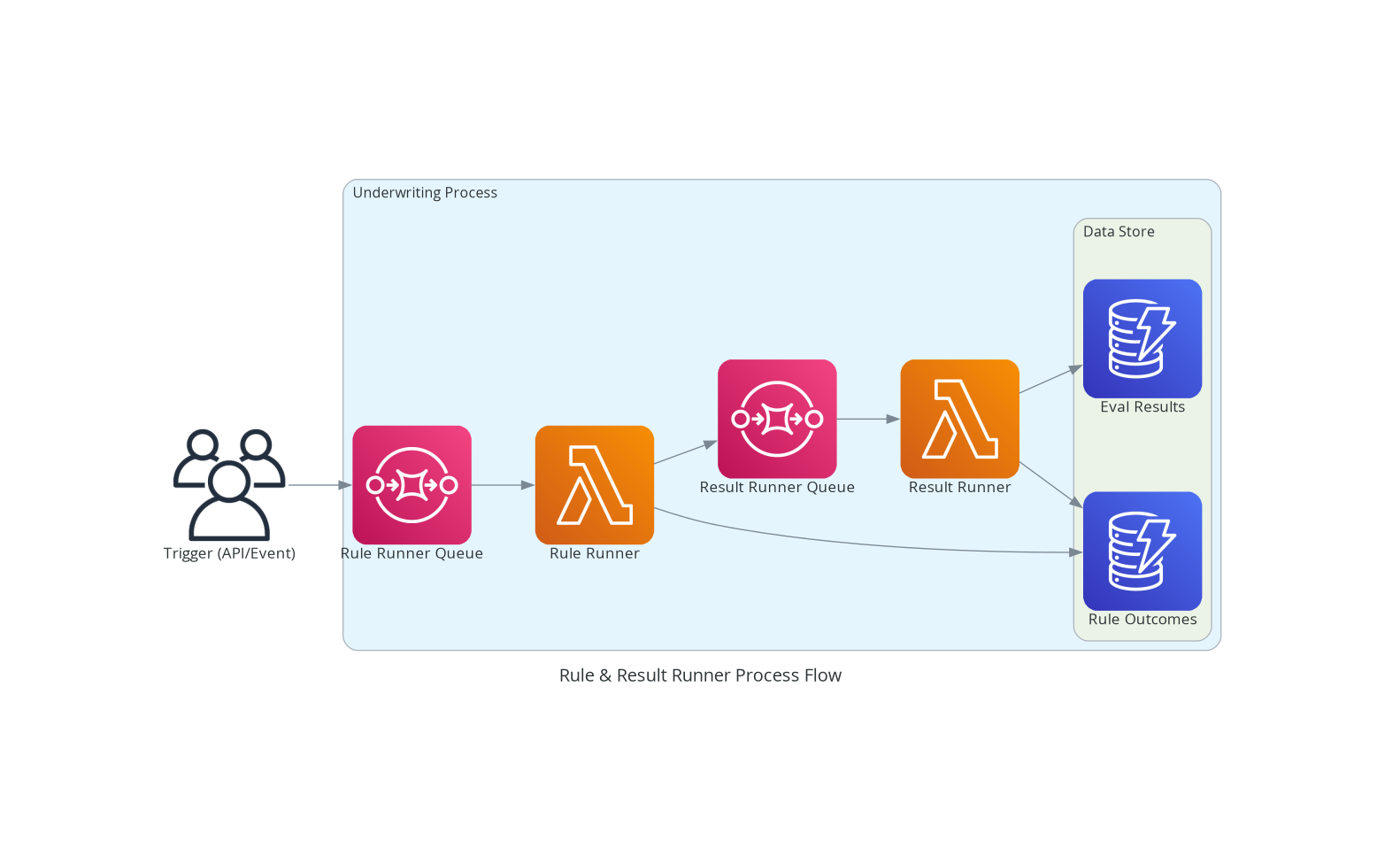
1. Trigger
The process is typically initiated by:
-
Event: A system event (e.g.,
account-updated) triggers a re-evaluation. -
API Request: Another service requests a re-evaluation because something important has changed for a user.
The trigger enqueues a message to the sqs-rule-runner queue.
2. Rule Runner (Execution)
The rule-runner Lambda consumes the message.
-
Data Gathering: Fetches necessary data from:
-
Float Service: Current float status, repayment history.
-
Transactions Service: Bank account transactions.
-
User Service: User profile and metadata.
-
Subscription Service: Membership status.
-
-
Rulebook Selection: Identifies the correct set of rules (Rulebook) to apply based on user segments or default configuration.
-
Rule Execution: Iterates through each rule in the rulebook.
-
Each rule calculates a specific outcome (Pass/Fail/Amount).
-
If a rule fails or errors, it is recorded.
-
-
Persistence: Writes individual Rule Outcomes to DynamoDB (
RULE_OUTCOME#<rule_name>). -
Handoff: Enqueues a message to the
rule-runner-queue(Result Runner Queue) indicating that rules have been run.
3. Result Runner (Aggregation)
The result-runner Lambda picks up the completion message.
-
Outcome Retrieval: Queries DynamoDB for all fresh Rule Outcomes for the user.
-
Aggregation Logic: Applies logic to combine individual rule results into a final decision.
-
Example: If any "Knockout" rule fails, the overall result is a denial.
-
Example: The approved amount is the minimum of all "Limit" rules.
-
-
Final Decision: Constructs the Evaluation Result object containing approved status and amounts for Floats and Loans.
-
Persistence: Saves the Evaluation Result to DynamoDB (
EVAL_RESULTS#…).-
This record is what the API retrieves to show the user their eligibility.
-